
Understanding contingent liabilities is vital for assessing the uncertainties that could affect a company’s financial position. These notes also provide insight into liability management, such as the terms of debt covenants or the fair value of derivative instruments. Debt covenants, embedded in loan agreements, impose restrictions on financial operations, affecting liquidity and flexibility. Understanding these terms is vital for assessing the company’s ability to meet obligations and avoid default. Additionally, notes may disclose guarantees or potential liabilities not yet reflected on the balance sheet, offering a clearer picture of financial risks.

Current liabilities
For example, XYZ Partnership obtains ₹1,000,000 long-term credit from a bank to support the development of another manufacturing unit. The credit has a ten-year repayment period and a 5% annual financing cost. Long-term obligations have long repayment durations and set borrowing fees. In that case, the company must recognise the accrued salaries as a liability in the December financial statements. Liabilities are an essential aspect of bookkeeping and play an important role in determining an organisation’s financial health.
Understanding Share-Based Compensation Plans: A Comprehensive Guide

Contingent liabilities are recorded in the accounts if the obligation is probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated. If the obligation is only possible but not probable, it is disclosed in the notes to the financial statements without recognition. Remote contingencies are liabilities accounts neither recorded nor disclosed, since the likelihood of payment is very low. There are also cases where there is a possibility that a business may have a liability. You should record a contingent liability if it is probable that a loss will occur, and you can reasonably estimate the amount of the loss. If a contingent liability is only possible, or if the amount cannot be estimated, then it is (at most) only noted in the disclosures that accompany the financial statements.
Pension Obligations
This approach ensures transparency while avoiding the overstatement of liabilities that may never materialize. A contingent liability is a potential liability that will only be confirmed as a liability when an uncertain event has been resolved at some point in the future. Only record a contingent liability if it is probable that the liability will occur, and if you can reasonably estimate its amount. Properly managing https://bosssheds.com/small-business-bookkeeping-step-by-step-guide-to/ a company’s liabilities is vital for maintaining solvency and avoiding financial crises. Understanding liabilities requires comprehending their classification and measurement.
- As the company makes payments on the mortgage, the principal portion of the payment reduces the mortgage payable, while the interest portion is accounted for as an interest expense.
- Understanding how liabilities fit into this equation helps in assessing a company’s financial structure and its reliance on borrowed funds.
- Also known as short-term liabilities, these are debts or money your business owes that needs to be paid off within a year.
- The current ratio evaluates a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations with its current assets.
- Current liabilities serve as a critical indicator of a company’s short-term solvency and its ability to generate enough cash to meet its obligations within the next twelve months.
Asset accounts example

When a future event is probable (likely to occur) AND Travel Agency Accounting you can reasonably estimate the amount, you should record the liability on your financial statements. For example, if your company loses a lawsuit and is just waiting for the judge to determine damages, you’d record your best estimate of those damages as a liability. Finally, watch out for off-balance-sheet arrangements that create effective liabilities without appearing on your balance sheet.
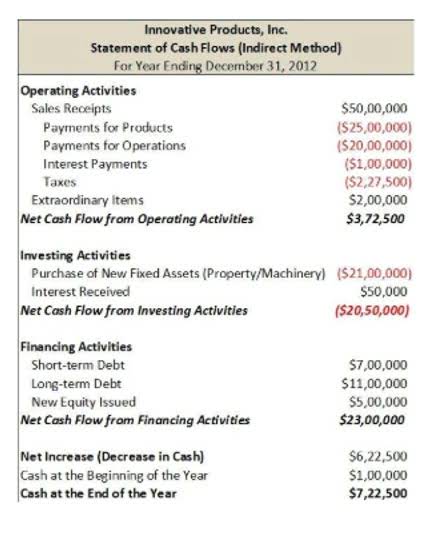
Financial liabilities are classified based on amortization of that particular liability by taking into account the fair value of the liability on profit or loss terms. A financial liability may also be classified based on the nature of that financial product. For example, some companies will list Accounts Payable as the first current liability account.
